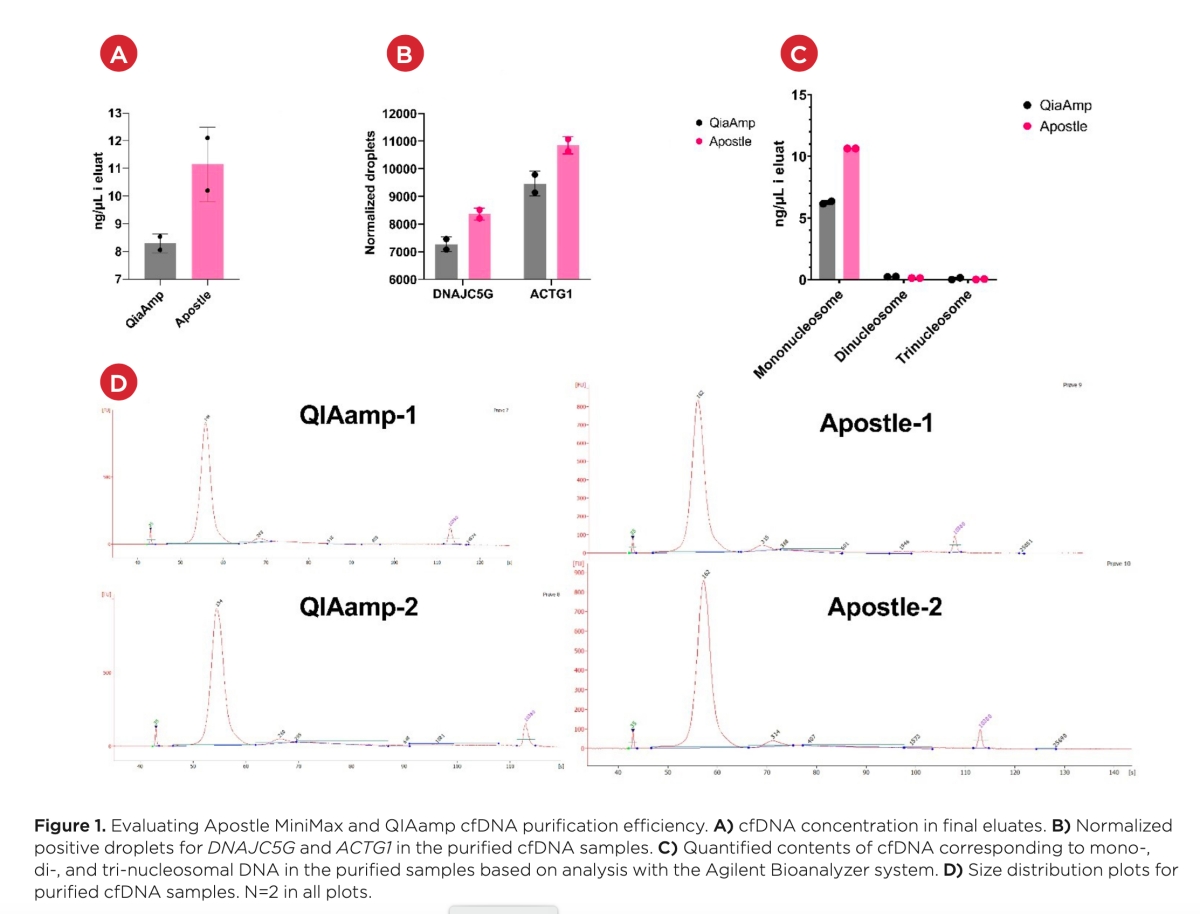
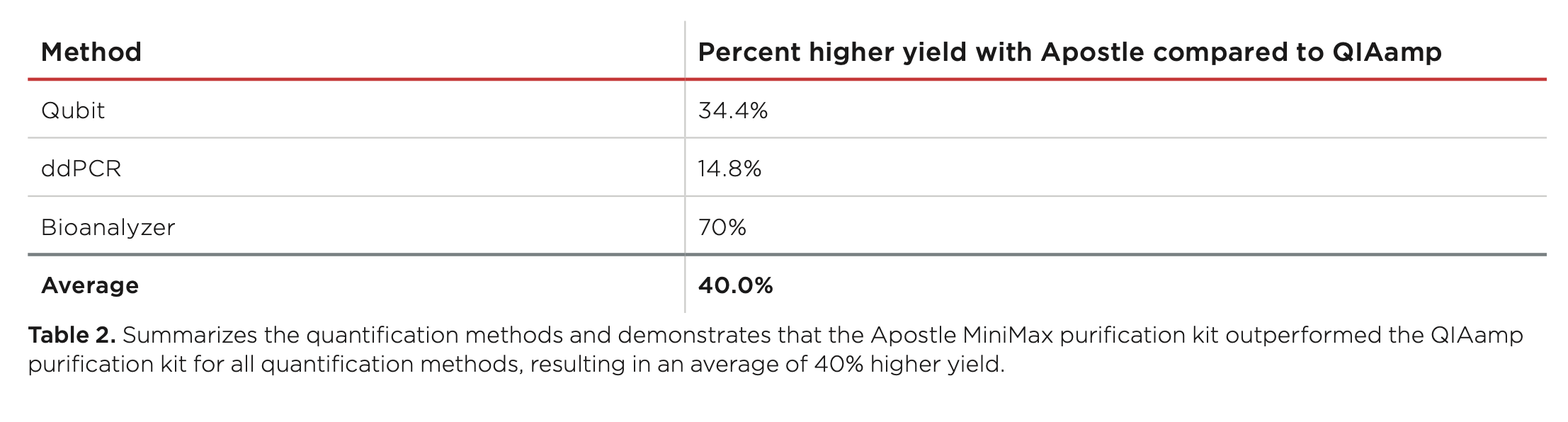
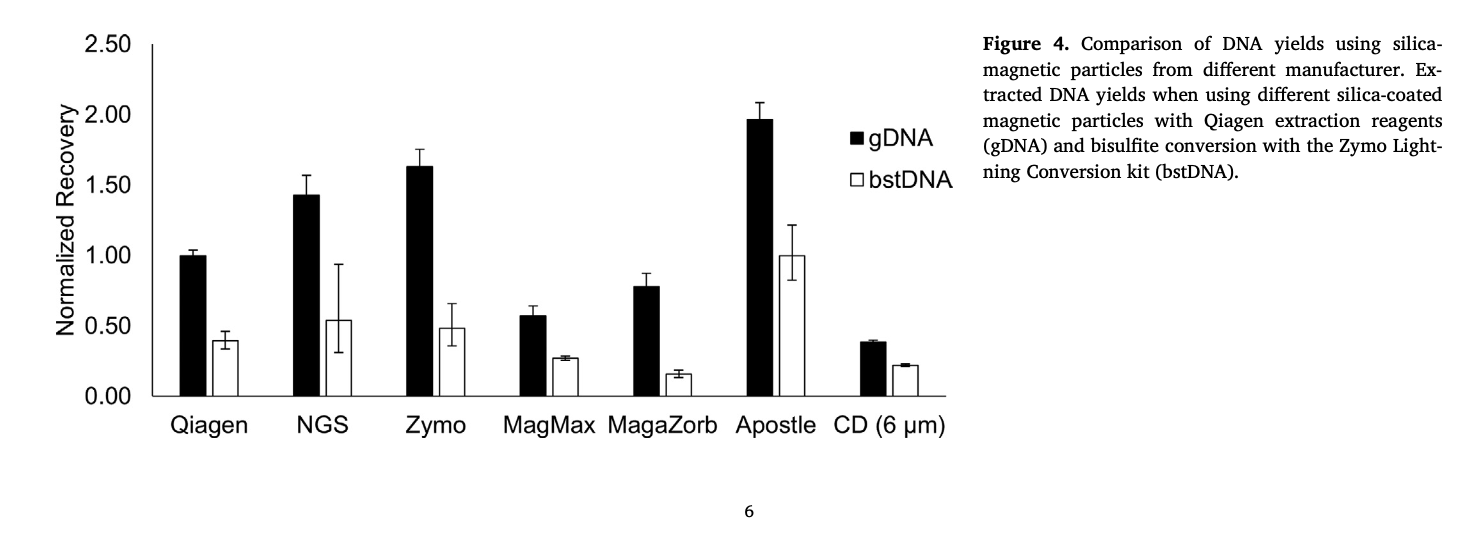
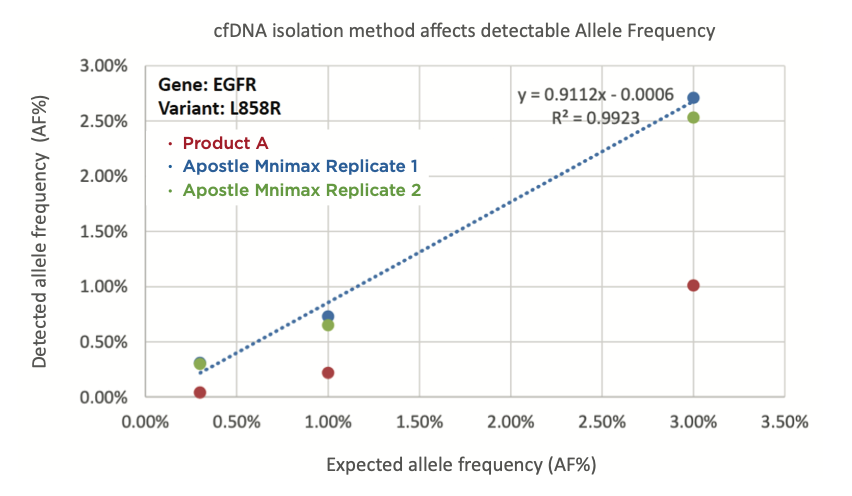
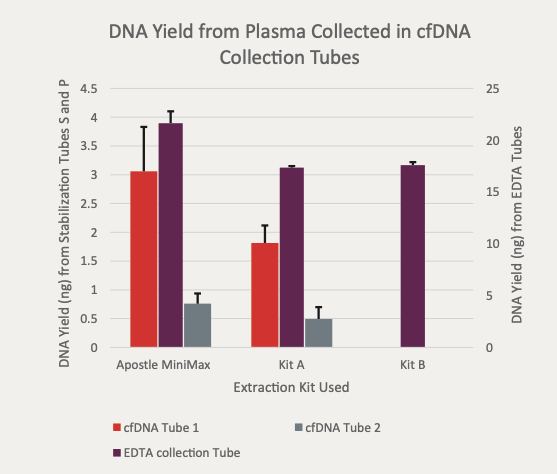
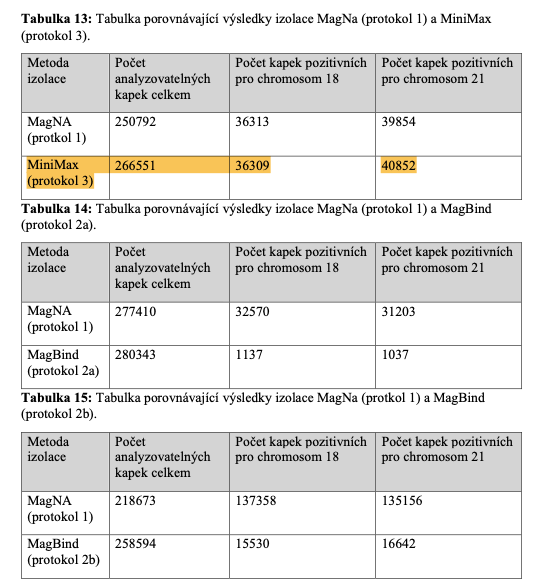
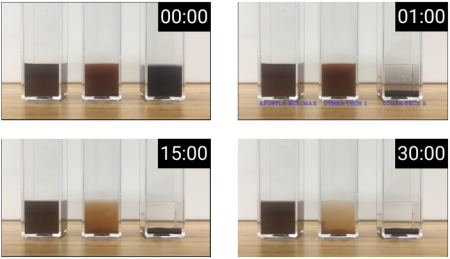
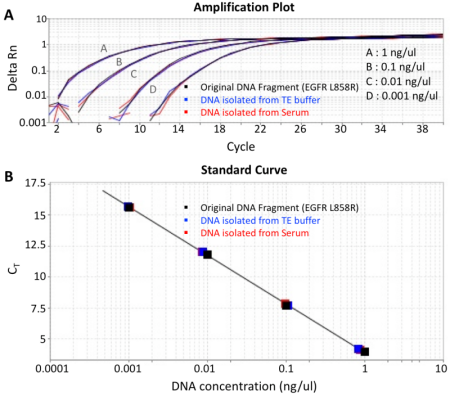
20 uL of DNA fragment containing the EGFR c.2573T>G L858R mutation (synthetic, ~170 bp), with concentration of 1 ng/uL, 0.1 ng/uL, 0.01 ng/uL, 0.001 ng/uL, was spiked into 1mL TE buffer (blue) or Serum (red) respectively. The mutated DNA fragment was isolated with Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit (Standard Edition), with a final elution volume of 20 uL. qPCR was performed using 1 uL of the isolated DNA, and compared with 1 uL of the corresponding original mutated DNA solution at 1 ng/uL, 0.1 ng/uL, 0.01 ng/uL, 0.001 ng/uL.
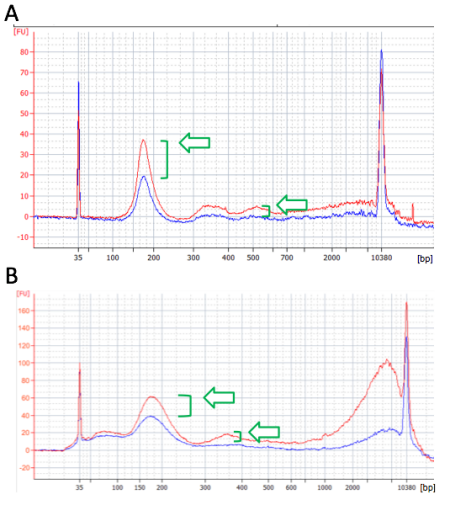
A) Amplification plot showing highly overlapping curves for mutated DNA fragment isolated with Apostle MiniMaxTM High Efficiency Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit and original DNA solution at different concentrations.
B) qPCR standard curve generated using original mutated DNA solution, in order to quantify the recovery of DNA isolated with Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit. DNA isolation recovery rate was calculated to be >90%.
Note: Displayed DNA concentration series at 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001 ng/ul are the concentrations of the original DNA dilution series before spiking into 1mL of serum. The corresponding DNA isolation working concentrations are 20 pg/ul, 2 pg/ul, 0.2 pg/ul, 0.02 pg/ul, respectively.