-
Products
Sectors
Categories
Product Information
- How to order
- [Flyer] MiniMax cfDNA Extraction & Automation (PDF)
- [Flyer] MiniMax cfRNA Extraction Solutions (PDF)
- [Flyer] MiniGenomics genomic DNA Isolation & Automation (PDF)
- [Flyer] MiniGenomics total RNA Isolation & Automation (PDF)
- [Flyer] miniEnrich DNA Purification & Size Selection Beads (PDF)
-
Technology
- Apostle MiniMax Technology (cfDNA)
- Apostle MiniMax Technology (cfRNA)
- Apostle MagTouch Technology
- Apostle BCT Technology
- Apostle MiniEnrich Technology
- Apostle MiniGenomics Technology
- Apostle MiniGenomics Technology (Stool)
- Apostle Triton Technology
- Apostle MiniMax (Type S)
- Apostle Viral RNA/DNA Isolation Automation System
- Apostle Well Plates and Accessories for Nucleic Acids Isolation
- How to choose a -86°C ULT Freezer
-
Applications
- Applications of Apostle Technologies
- By Therapeutic Areas or Methods
- Oncology
- NIPT (Noninvasive Prenatal Testing)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Virology & Public Health
- Cardiovascular Research
- NGS (Next-Gen Sequencing)
- DNA Methylation Analysis
- cfRNA Analysis
- ddPCR (Droplet Digital PCR)
- rtPCR (Real Time PCR)
- cfChIP (cell-free Chromatin Immunoprecipitation)
- Clinical Trial
- Sign In
Why Apostle
Laboratory costs are high. Apostle supports our community with high-quality, cost-effective, and eco-friendly products:
That’s why more and more research and clinical laboratories are now switching to Apostle technologies.
- Superior performance
- Minimum 50% of savings on cost
- Top-notch technical support
- Environment-friendly / Save mother nature
- Extensively validated and cited [Ref]
That’s why more and more research and clinical laboratories are now switching to Apostle technologies.
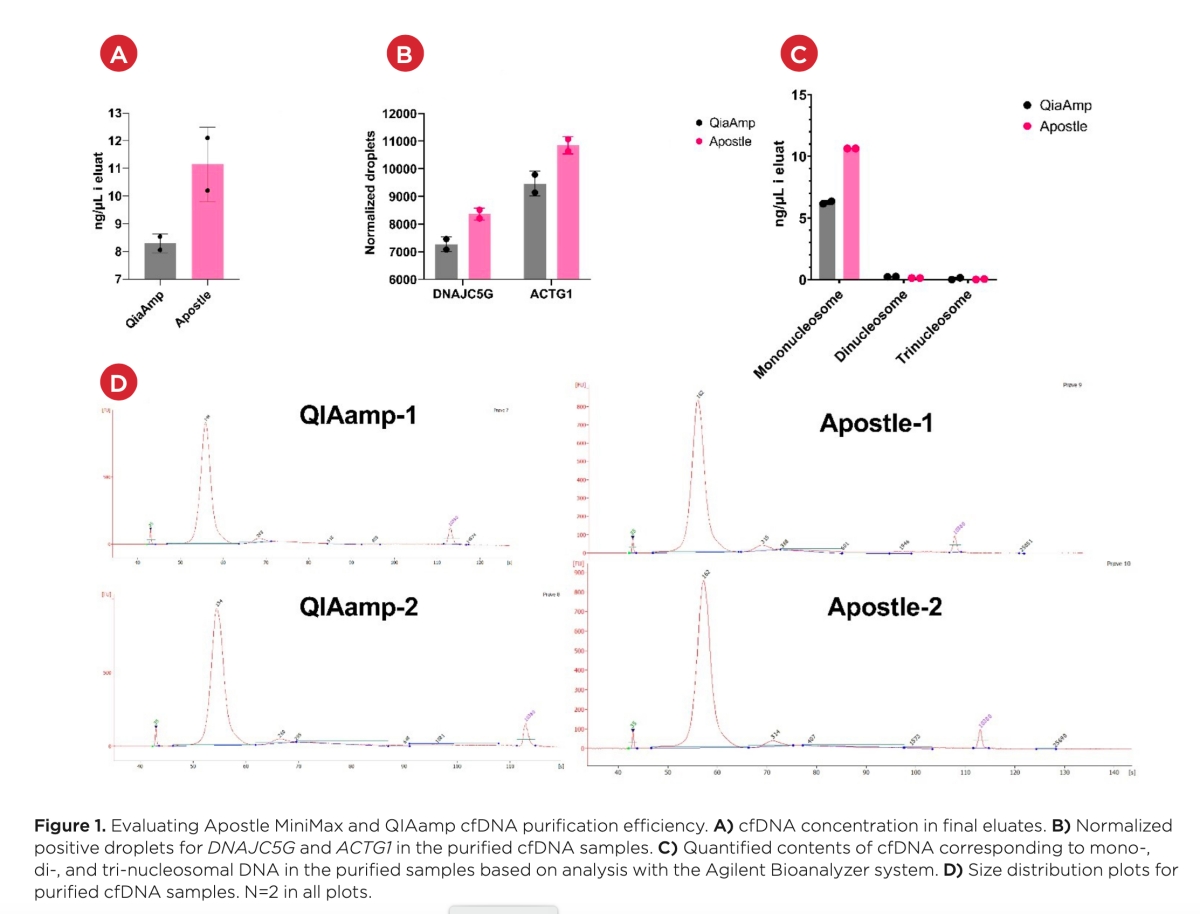
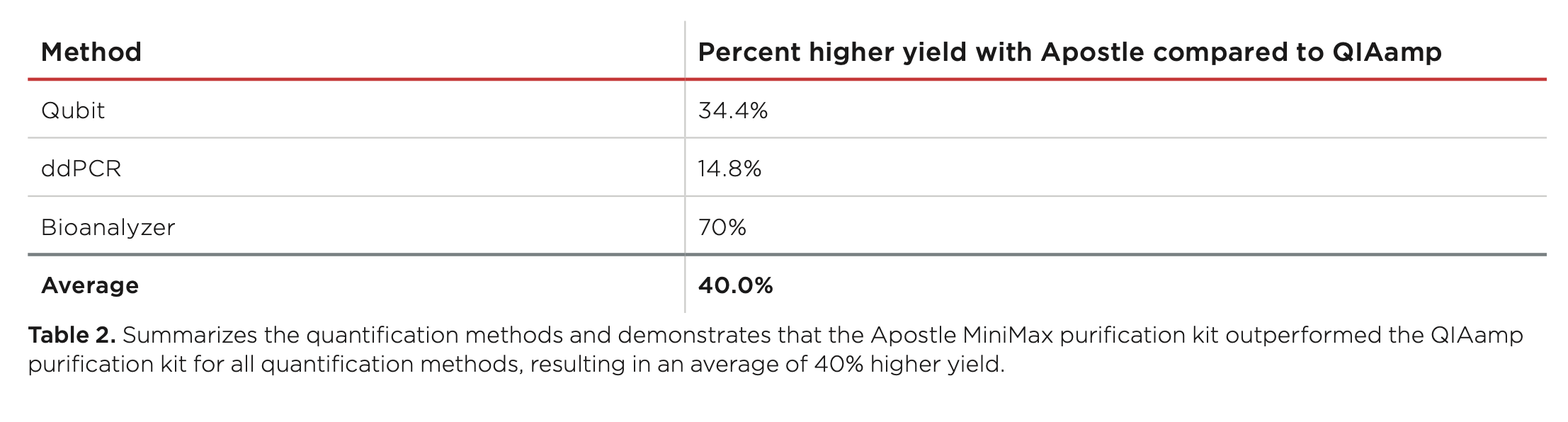
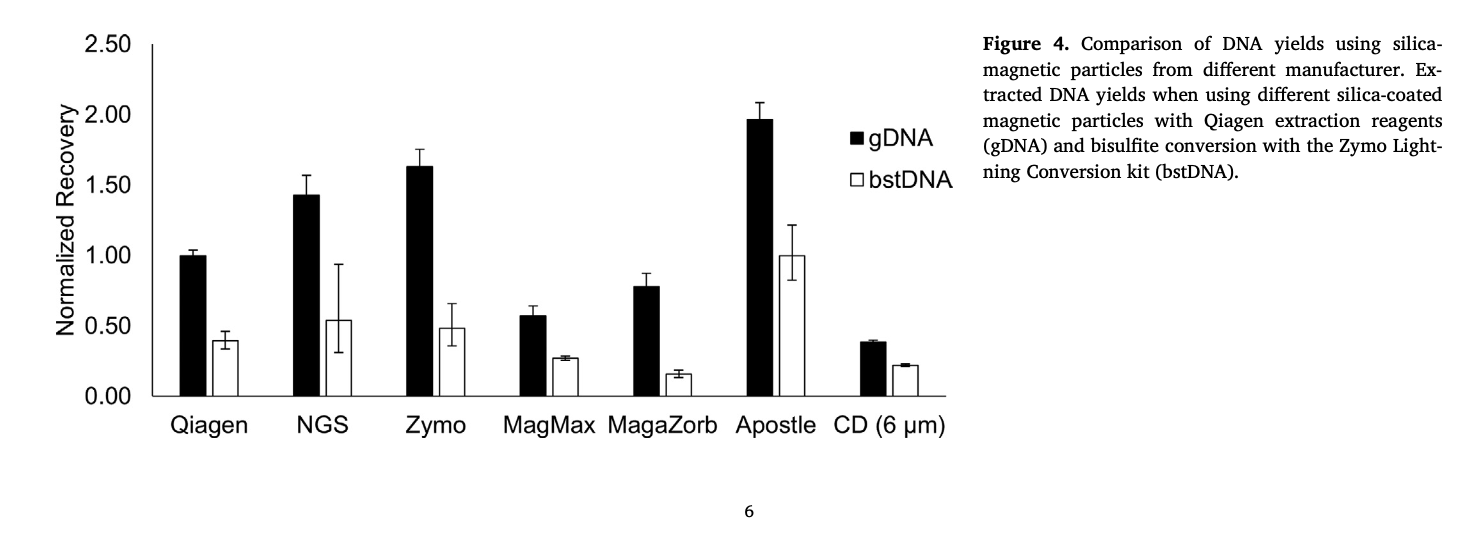
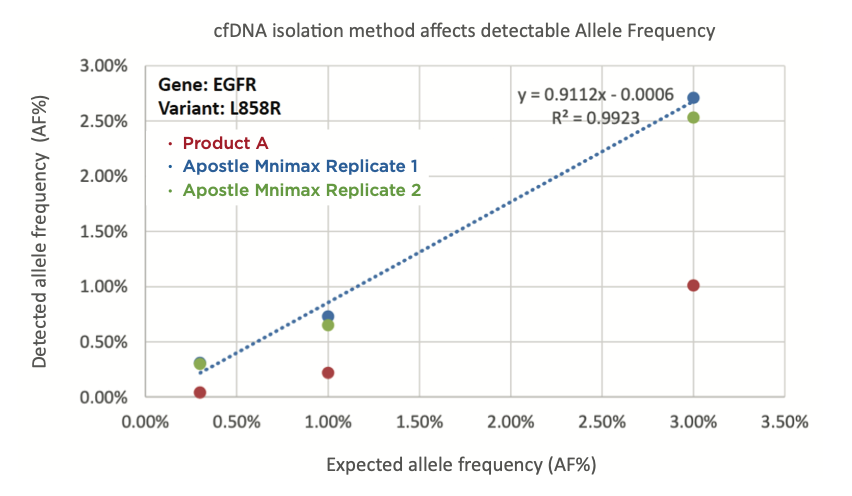
Best-in-Class Performance in cfDNA Isolation: Side by Side Comparison
Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency Cell-Free DNA Isolation Kit
The ability to isolate and analyze circulating cell free DNA (cfDNA) at very low concentrations is becoming increasingly important, particularly in non-invasive prenatal test (NIPT), early cancer detection, and infectious disease diagnosis. Highly efficient isolation of cfDNA from complexed biological medium is a crucial step for subsequent cfDNA analysis.
Apostle MiniMax technology offers a best-in-class efficiency and purity compared with conventional technologies to capture and isolate the circulating cell-free genetic materials. Its superb performance has been extensively validated.
As used by our clients in:
As used by our clients in:
- Tumor- and circulating-free DNA methylation identifies clinically relevant small cell lung cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2024;42(2):225-237
- A shared neoantigen vaccine combined with immune checkpoint blockade for advanced metastatic solid tumors: phase 1 trial interim results. Nature Medicine 2024; 30: 1013–1022
- Integrative modeling of tumor genomes and epigenomes for enhanced cancer diagnosis by cell-free DNA. Nature Communications 2023;14:2017
- Simultaneous analysis of mutations and methylations in circulating cell-free DNA for hepatocellular carcinoma detection. Science Translational Medicine 2022;14:672
- Safety and tolerability of AAV8 delivery of a broadly neutralizing antibody in adults living with HIV: a phase 1, dose-escalation trial. Nature Medicine 2022; 28:1022-1030
- More ...
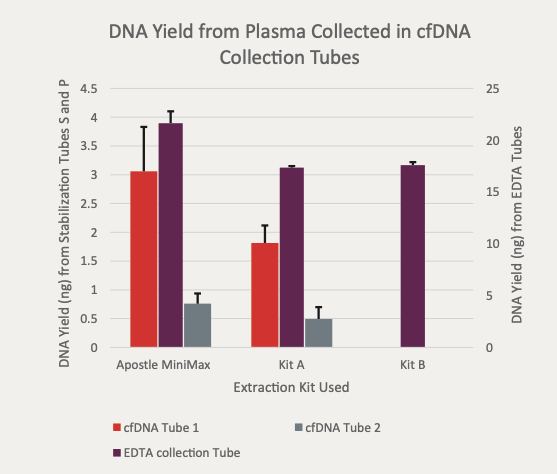
Apostle MiniMax Cell-Free DNA Blood Collection Tube
Powered by Apostle MiniMax technology, Apostle MiniMax cfDNA Blood Collection Tube (BCT) is an excellent tool for blood cfDNA preservation during blood collection, storage and transport.
This is achieved through Apostle MiniMax cfDNA BCT’s ability to:
As used by our clients in:
This is achieved through Apostle MiniMax cfDNA BCT’s ability to:
- Prevent the release and contamination of genomic DNA from cells in blood during storage and transportation.
- Preserve existing cfDNA in blood from degradation.
- Prevent existing cfDNA in blood from cross-linking with with other biomolecules (i.e. protein).
As used by our clients in:
- Integrated analysis of oral rinse-derived and plasma circulating tumour DNA for mutation profiling and outcome prediction with oral squamous cell carcinoma. npj Precision Oncology Volume 9, 13 June 2025, 183.
- SneakPeek Test (as OEM supplier)
- Evaluation and integration of cell-free DNA signatures for detection of lung cancer. Cancer Letters Volume 604, 1 November 2024, 217216.
- A novel SNP-based approach for non-invasive prenatal paternity testing using multiplex PCR targeted capture sequencing. Journal of Translational Genetics and Genomics 2024;8:378-93.
- More ...
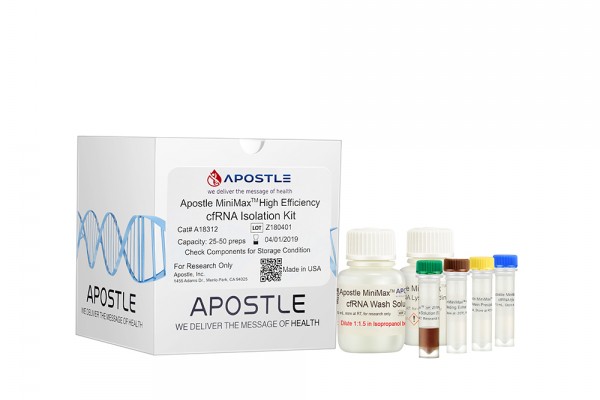
Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency Cell-Free RNA Isolation Kit
Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency cfRNA Isolation Kit offers superior isolation efficiency of cell-free RNAs between 17 nt to 1000 nt, without phenol or chloroform. it is ready for a broad range of subsequent applications, including sequencing, PCR, etc. It is suitable for processing samples collected in various major blood collection tubes, especially which will prevent RNA degradation during storage.
As used by our clients in:
As used by our clients in:
- Diagnostic and prognostic potential of cell-free RNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma for brain tumors. npj Precision Oncology 9, Article number: 123 (2025).
- Terminal modifications independent cell-free RNA sequencing enables sensitive early cancer detection and classification. Nature Communications 15, Article number: 156 (2024).
- Comprehensive characterization of small noncoding RNA profiles in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (HPH) rat tissues. iScience 2024 Feb 16; 27(2): 108815.
- More ...
Apostle MiniMax High Efficiency Total cfDNA/cfRNA (cfNAs) Isolation Kit
Apostle MiniMax cfDNA/cfRNA isolation kit is featured for its efficient recovery of cfDNA in the range between 50-3000bp and cfRNA in the range between 17-1000 nt, and the isolated nucleic acids can be applied for NGS and PCR-based downstream applications.
Features:
As used by our clients in:
Features:
- Superior isolation efficiency without using phenol or chloroform
- Recovery of cfDNA /cfRNA in the one sample
As used by our clients in:
- Liquid Biopsy for Evaluating Mutations and Chromosomal Aberrations in Cerebrospinal Fluid from Patients with Primary or Metastatic Central Tumors. The Journal of Liquid Biopsy (2024).
- Combining cell-free RNA with cell-free DNA in liquid biopsy for hematologic and solid tumors. Heliyon 9 (2023) e16261; May 16, 2023.
- More ...
High Quality, Cost Effective Lab Consumables
Costs of laboratory consumables can be high. Apostle serves our community with high-quality, cost-effective, Apostle-branded laboratory consumables. We are proud to be a supplier for many world-renowned universities and health centers including Stanford University, UCSF, UC Berkeley, University of Texas, etc.
- Cell biology series
- Molecular biology series
- Liquid handling series
- Sample collection and processing series
- Comprehensive product line coverage with 900+SKU
- High quality
- Cost-effective. Guaranteed to save 30% cost or more.
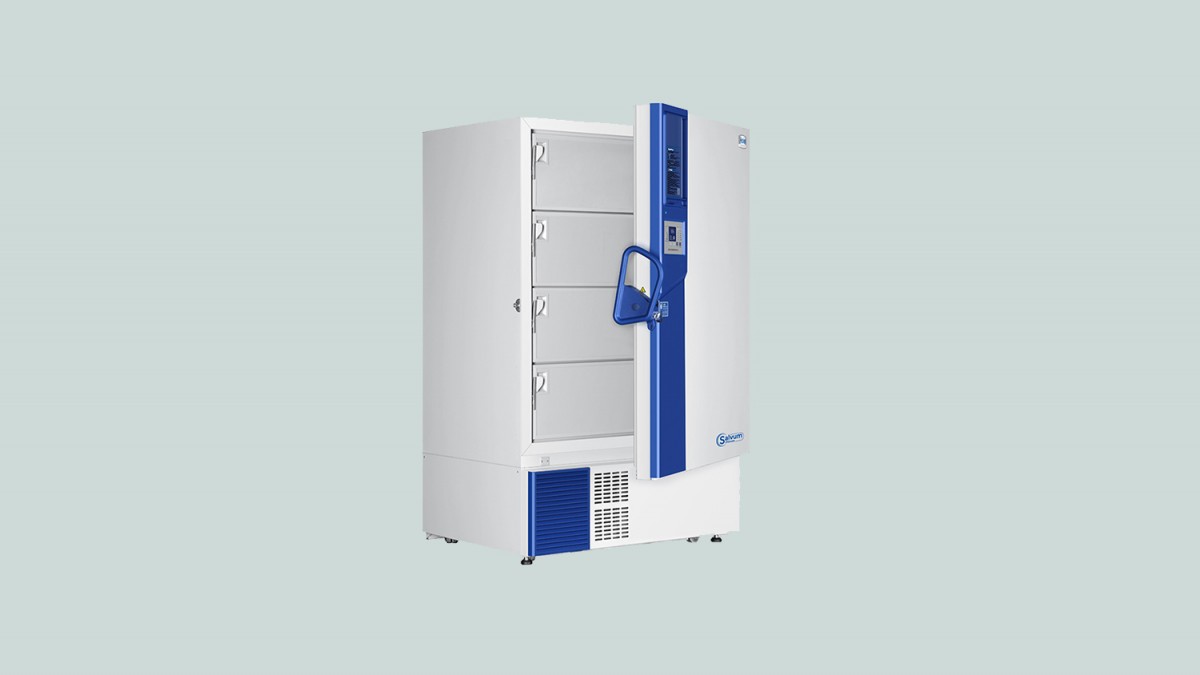
Haier Biomedical Lab Freezers, Energy Star (-30C, -86C)
Haier Biomedical Lab Freezers feature a built-in evaporator, large storage space, and adjustable shelfs, providing faster temperature pulldown, and a better temperature uniformity of set point +/- 3°C. It is suitable for sample storage within blood banks, hospitals, disease control centres, research institutes, electronic, chemical and other industries, cryopreservation of plasma, biologics and other products, also suitable for cold tests for components and materials.
Apostle is a proud supplier and distributor of Haier Biomedical Freezers to many world-leading institutes including Stanford University, UCSF, Washington University in St. Louis.
Apostle is a proud supplier and distributor of Haier Biomedical Freezers to many world-leading institutes including Stanford University, UCSF, Washington University in St. Louis.
- Energy-efficient Variable Frequency Inverter Technology
- Large Capacity Storage with Excellent Temperature Uniformity
- Low Noise
- Environment Friendly
- No. 1 best selling brand in Asia. Top 3 globally. Top quality.
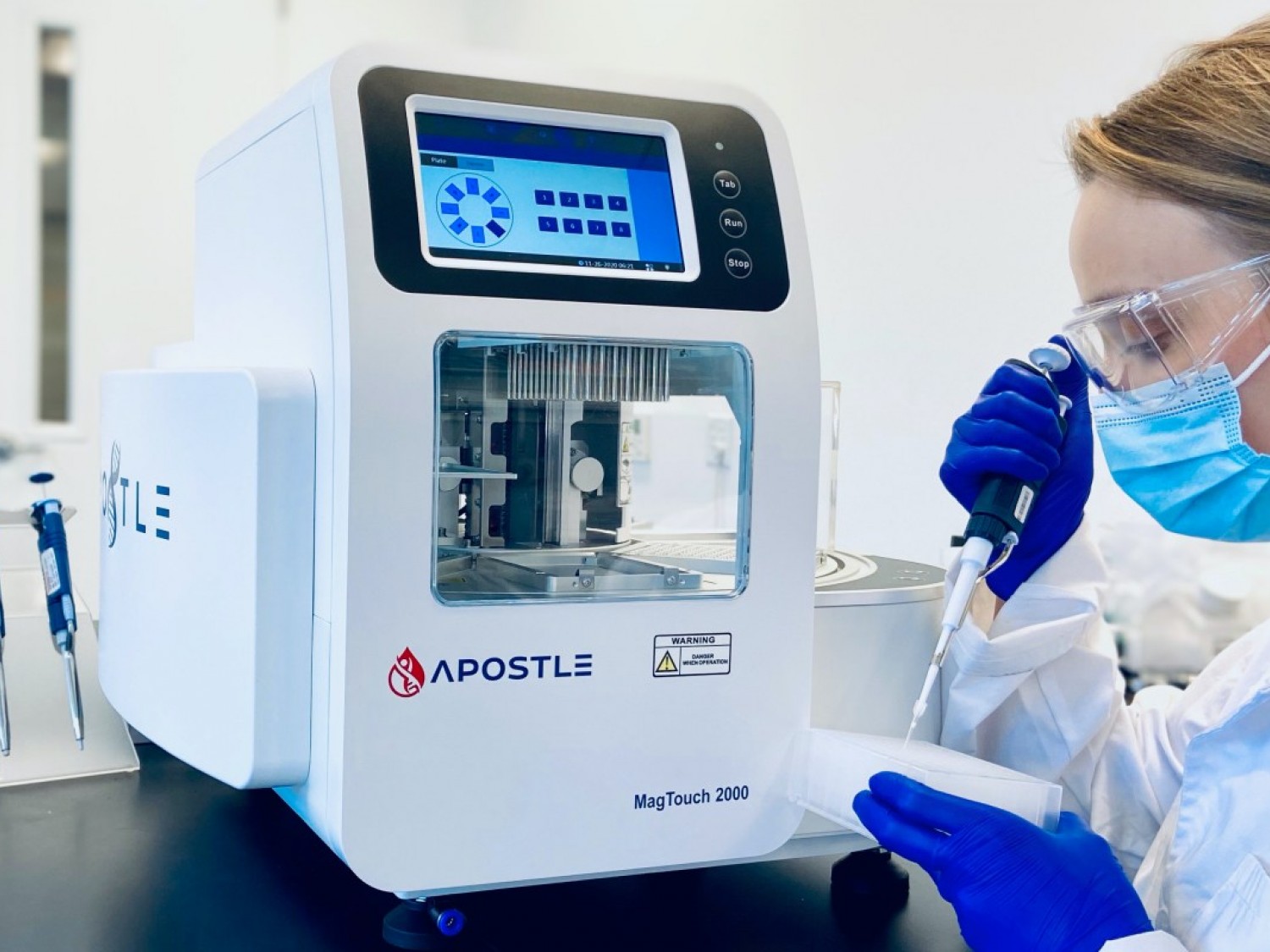
MagTouch 2000
The MagTouch 2000 instrument is an automatic extraction and purification system for nucleic acids from various types of biological samples collected in multiple transport media, including extraction for cfDNA. It can absorb, transfer and release magnetic beads by a magnetic rod and magnetic rod sleeve to separate magnetic beads and samples. The operation is automatic, fast and simple.
Highlighted Features
Highlighted Features
- Extremely robust and reliable; sustained 7x24 heavy use for 2+ years in very busy clinical laboratory environment. Notably, MagTouch 2000 has processed over 20 million samples during the COVID-19 pandemic, helping our community fight the global infectious disease.
- Cost-effective; guaranteed 30% or more savings than other products
- High-efficiency and high-throughput
- Small footprint on the desktop
- FDA document involving MagTouch 2000 As used by our clients in:
- Rapid repeat infection of SARS-CoV-2 by two highly distinct delta-lineage viruses. Andrew J. Gorzalski , Christina Boyles, Victoria Sepcic, et al. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2022; 104(1): 115747
- Evaluation and integration of cell-free DNA signatures for detection of lung cancer. Cancer Letters Volume 604, 1 November 2024, 217216.
- More ...
Apostle MiniGenomics Stool DNA Isolation Kit
Apostle MiniGenomics® Stool DNA Isolation Kit is designed for rapid extraction and purification of high-quality, ready-to-use genomic DNA and/or bacterial DNA from fresh or frozen stool samples.
As used by our clients in:
- Advanced magnetic nanoparticle technology for superior DNA adsorption and release
- Standard purification methods suitable for biological samples in various forms or reagents
- Specialized reagents to enhance DNA quality from challenging samples
- Compatible with multiple high-throughput automated nucleic acid extraction platforms
As used by our clients in:
- Intestinal microbiota as biomarkers for different colorectal lesions based on colorectal cancer screening participants in community. Front. Microbiol. 06 February 2025. Volume 16.
- Combined detection of SDC2/ADHFE1/PPP2R5C methylation in stool DNA for colorectal cancer screening. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology June 03, 2023.
- A systematic evaluation of stool DNA preparation protocols for colorectal cancer screening via analysis of DNA methylation biomarkers. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2021; 59(1): 91–99.
- CE marked colon cancer test kits (as OEM supplier)
- More ...
Apostle MiniEnrich Short Fragments Enrichment Kit
Precise DNA sizing can boost sequencing efficiency, reduce cost, improve data quality, and even allow sequencing of low-input samples, while current pervasive DNA sizing approaches are incapable of differentiating DNA fragments under 200 bp with high resolution (<20 bp). The Apostle MiniEnrich Short Fragments Enrichment Kit is a simple, automatable, high-resolution DNA size enrichment workflow on a magnetic nano-platform to exploit this 20 bp size difference and to enrich fetal DNA fragments from maternal blood.
As published in:
As published in:
Apostle MiniEnrich Carboxyl Beads for Purification (AMPure XP alternative)
Next-generation purification, size selection, and long-read size selection.
The Apostle MiniEnrich Purification Beads is designed for purification and clean-up of DNA fragments from the contaminants in NGS and molecular biology workflows. It can be used on samples after DNA isolation, fragmentation, PCR amplification, cloning, library preparation, etc. With proprietary Apostle MiniEnrich technology, the kit is featured for its more efficient removal of contaminants and recovery of DNA fragments of interest than current market-leading products. This product is an effective alternative to AMPure XP, a brand name owned by Beckman Coulter. This product is not manufactured by Beckman Coulter.
As published in:
The Apostle MiniEnrich Purification Beads is designed for purification and clean-up of DNA fragments from the contaminants in NGS and molecular biology workflows. It can be used on samples after DNA isolation, fragmentation, PCR amplification, cloning, library preparation, etc. With proprietary Apostle MiniEnrich technology, the kit is featured for its more efficient removal of contaminants and recovery of DNA fragments of interest than current market-leading products. This product is an effective alternative to AMPure XP, a brand name owned by Beckman Coulter. This product is not manufactured by Beckman Coulter.
As published in:
RiboCraft Alpha Transfection Reagent
RiboCraft Alpha Transfection Reagent is a one-of-a-kind transfection reagent, uniquely suited for both in vitro and in vivo RNA transfection. Coming from research results at Stanford University, this dual-function capability is a rare find in the market, offering unparalleled convenience and efficiency for researchers exploring the frontiers of genetic manipulation. RiboCraft Alpha provides any research program the unique ability to directly translate from cell-based assays to animal studies. RiboCraft Alpha stands out from the crowd with:
- Dual-function capability: Efficiently delivers RNA both in vitro and in vivo
- Versatility: Supports a wide range of RNA cargos, including mRNA, siRNA, and gene-editing tools
- Robustness: Consistent and reliable performance across diverse cell lines and animal models
What our community say
News
Latest Updates on Social Media
May 18, 2025
About Us
Apostle Inc is a biotechnology company in Pleasanton, CA, a provider of innovative technologies and services for public health and life sciences. Apostle develops and provides best-in-class nucleic acid isolation and preservation technologies, including innovative technologies in the space of liquid biopsy - the sampling and analysis of non-solid biological tissue, primarily blood, often utilizing circulating free DNA (cfDNA) as a biomarker. Apostle technologies have been applied in many world-class R&D studies, clinical laboratory settings, and public health response and surveillance. To date, over 20 million samples have been successfully processed using our technologies, and the number is quickly growing.














































































-300x200h.jpg)
-78-01-300x200w.jpg)














































































 In May 2025, npj Microgravity (Nature Publishing Group) published a landmark paper led by Baylor College of Medicine’s Human Genome Sequencing Center, establishing the first official manual for astronaut bio-specimen collection in U.S. commercial space missions. The GENESTAR manual — developed with data from the Axiom-2 mission (via SpaceX and Axiom Space) — includes protocols for collecting blood, plasma, cfDNA, RNA, PBMCs, and more. A total of 339 astronaut samples were collected.
In May 2025, npj Microgravity (Nature Publishing Group) published a landmark paper led by Baylor College of Medicine’s Human Genome Sequencing Center, establishing the first official manual for astronaut bio-specimen collection in U.S. commercial space missions. The GENESTAR manual — developed with data from the Axiom-2 mission (via SpaceX and Axiom Space) — includes protocols for collecting blood, plasma, cfDNA, RNA, PBMCs, and more. A total of 339 astronaut samples were collected.

